Notice: Trying to access array offset on value of type null in /srv/pobeda.altspu.ru/wp-content/plugins/wp-recall/functions/frontend.php on line 698
At Finance Strategists, we partner with financial experts tax deductions for owner to ensure the accuracy of our financial content.
About Dummies
All such information is provided solely for convenience purposes only and all users thereof should be guided accordingly. This formula is critical for understanding how actual spending tracks against estimations. Dummies has always stood for taking on complex concepts and making them easy to understand. Dummies helps everyone be more knowledgeable and confident in applying what they know.
Direct Material Quantity Variance
This investigative approach ensures that corrective actions are targeted and effective. Supplier performance also plays a crucial role in direct material variance. Reliable suppliers who consistently deliver quality materials at agreed-upon prices help maintain stable production costs. Conversely, issues such as late deliveries, substandard materials, or unexpected price hikes can lead to variances. Building strong relationships with suppliers and regularly evaluating their performance can help businesses anticipate and address potential problems before they impact production.
Formulas to Calculate Material Cost Variance and Material Price Variance
Take self-paced courses to master the fundamentals of finance and connect with like-minded individuals. Ask a question about your financial situation providing as much detail as possible. Our goal is to deliver the most understandable and comprehensive explanations of financial topics using simple writing complemented by helpful graphics and animation videos.

What is the formula for the direct materials price variance?
During the recent period, Teddy Bear Company purchased 20,000 bags of stuffing material for manufacturing stuff toys. Yes, even a positive variance can mean problems like lower quality materials being used. It shows if you are spending more or less on materials than expected, which affects profits. This team of experts helps Finance Strategists maintain the highest level of accuracy and professionalism possible. The articles and research support materials available on this site are educational and are not intended to be investment or tax advice.
- AI algorithms can analyze historical data to predict future material needs more accurately, helping businesses plan better and avoid unexpected variances.
- As you can see from the list of variance causes, different people may be responsible for an unfavorable variance.
- Companies must stay informed about market trends and consider strategies such as hedging or long-term contracts to mitigate these risks.
- The direct material price variance can be meaningless or even harmful in some circumstances.
The actual quantity of direct materials at standard price equals $310,500. A favorable materials quantity variance indicates savings in the use of direct materials. An unfavorable variance, on the other hand, indicates that the amount of materials used exceeds the standard requirement. The purchasing staff of ABC International estimates that the budgeted cost of a chromium component should be set at $10.00 per pound, which is based on an estimated purchasing volume of 50,000 pounds per year. During the year that follows, ABC only buys 25,000 pounds, which drives up the price to $12.50 per pound. This creates a direct material price variance of $2.50 per pound, and a variance of $62,500 for all of the 25,000 pounds that ABC purchases.
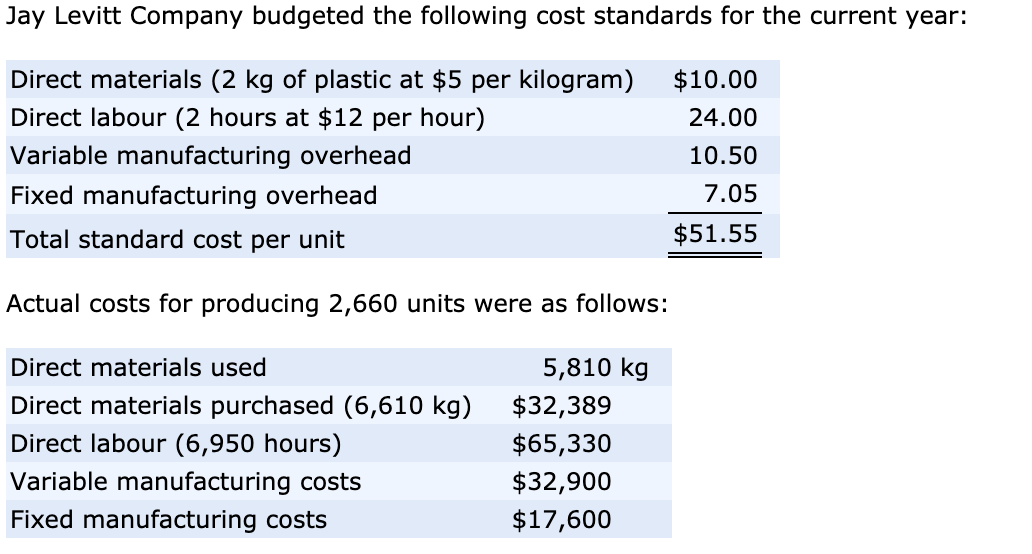
For example, a rush order is probably caused by an incorrect inventory record that is the responsibility of the warehouse manager. As another example, the decision to buy in different volumes may be caused by an incorrect sales estimate, which is the responsibility of the sales manager. In most other cases, the purchasing manager is considered to be responsible. Direct material price variance measures how much more or less you spent on materials compared to your plan. Your aim should be a thorough and error-free record of every raw material that goes into your products. Using the materials-related information given below, calculate the material variances for XYZ company for the month of October.
In a multi-product company, the total quantity variance is divided over each of the products manufactured. If Fresh PLC values its stock on FIFO or other actual cost basis, then the variance may be calculated on the quantity consumed during the period. The following sections explain how management can assess potential causes for a favorable or adverse material price variance and devise a suitable response to the variation. Finance Strategists is a leading financial education organization that connects people with financial professionals, priding itself on providing accurate and reliable financial information to millions of readers each year. Knowledge of this variance may prompt a company’s management team to increase product prices, use substitute materials, or find other offsetting sources of cost reduction. As you can see from the list of variance causes, different people may be responsible for an unfavorable variance.
Not necessarily; some variances are normal, but big ones need investigation to find the cause and fix it. This suggests spending more and hints at possible issues with purchasing decisions or market changes. Now, let’s delve into an example to better understand how the calculator functions.
For example, IoT sensors can monitor the exact amount of material used in each production cycle, allowing for precise adjustments and reducing waste. AI algorithms can analyze historical data to predict future material needs more accurately, helping businesses plan better and avoid unexpected variances. As the inventory is valued on standard cost, the material price variance must take the effect of the cost difference on entire quantity purchased during the period.
Another advanced technique is the application of statistical methods, such as regression analysis, to understand the relationship between different variables affecting material costs. By analyzing historical data, businesses can identify key drivers of variances and quantify their impact. For example, regression analysis might reveal that a 10% increase in supplier lead time results in a 5% increase in material quantity variance. Armed with this knowledge, companies can focus their efforts on improving supplier lead times to achieve better cost control. Additionally, the use of variance decomposition allows businesses to break down complex variances into more manageable components, providing deeper insights into specific areas of concern.